Diploma Thermal Engineering 2 three marks pdf
Dear Students
Diploma Thermal Engineering 2 three marks Welcome to Diploma Exam Corner, We have added Diploma Thermal Engineering 2 three marks pdf. You can download Diploma Thermal Engineering 2 three marks pdf for the unit 1 as pdf
| Name of the subject | Thermal Engineering 2 |
| Name of the Unit | Unit 1 |
| Scheme | N Scheme |
| Syllabus | Tamilnadu Diploma Syllabus |
| Study Material | Three Marks |

Diploma Thermal Engineering 2 three marks pdf
- What is steam?
Steam is a vapour produced by the evaporation of water when water is heated in a container.
2. Mention the various stages in the formation of steam.
1) Solid stage 2) Melting stage 3) Liquid stage 4) Vapourising stage 5) Superheating stage
3. What is saturation temperature?
The temperature at which the water begins to boil during heat addition is known as saturation temperature or generation temperature. At the atmospheric pressure, the saturation temperature of water is 100oC.
4. Define enthalpy of water?
It is also called as sensible heat of water or liquid enthalpy. Enthalpy of water is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of unit mass of water from 0oC to saturation temperature under constant pressure.
5. What is latent heat of water or enthalpy of evaporation.
Latent heat of water or enthalpy of evaporation is defined as the amount of heat required to completely convert 1 kg of water at saturation temperature into dry steam.
6. State the conditions of steam.
a) Wet steam : If the steam contains moisture or suspended water particles, then it is called as wet steam.
b) Dry saturated steam : When the wet steam is further heated, a stage will be reached when all the water particles are converted into steam. This is called dry steam or dry saturated steam.
c) Superheated steam : When heat is added to dry saturated steam at constant pressure, the temperature rises above saturation temperature. The steam thus obtained is called superheated steam.
7. Define superheat enthalpy and degree of superheat.
The heat supplied to the superheated steam above the saturation temperature is known as heat of superheat or superheat enthalpy. The difference between the temperature of superheated steam ( sup t ) and saturation temperature of dry steam is called as degree of superheat.
8. State the advantages of superheated steam.
1) Thermal efficiency is increased due to the high temperature of super heated steam.
2) More work can be obtained by using super heated steam as it contains more heat energy.
3) A heat loss due to condensation of steam on cylinder walls is reduced
. 4) Erosion and corrosion of turbine blade is eliminated while using super heated steam.
5) The plant capacity is increased. 9. Define dryness fraction. The dryness fraction of steam is defined as the ratio of mass of dry saturated steam to the total mass of wet steam containing it. It is represented by ‘ x ’.
11. Define enthalpy of wet steam.
Enthalpy of wet steam is the amount of heat required to convert 1 kg of water at 0oC into wet steam at constant pressure. It is denoted by the symbol ‘ hwet ’. ).( fwet += hxhh fg kJ/kg
12. Define enthalpy of dry saturated steam.
Enthalpy of dry saturated steam is the amount of heat required to convert 1 kg of water at 0oC into dry steam at constant pressure. It is denoted by the symbol ‘ hg ’. += hhh fgfg kJ/kg
13. Define enthalpy of superheated steam.
Enthalpy of superheated steam is the amount of heat required to convert 1 kg of water at 0oC into superheated steam at constant pressure. It is denoted by the symbol ‘ hsup ’.
14. Write the formula for enthalpy of superheated steam
Enthalpy of dry steam (kJ/kg) Cps = Specific heat of superheated steam (kJ/kgK) sup t = Temperature of superheated steam (oC) s t = Saturation temperature (oC)
15. Define critical point.
The critical point is the point at which the water is directly converted into dry steam without taking latent heat. 16. Define critical temperature and critical pressure. The critical temperature is defined as the temperature above which a substance cannot exist as a liquid. The critical pressure is define as the pressure above which a substance cannot exist in liquid state when it is at critical temperature. 17. Write the critical conditions of water. 1. Freezing temperature of water at atmospheric pressure = 0oC = 273.15 K 2. Boiling temperature of water at atmospheric pressure = 100oC = 373.15 K
16. Define critical temperature and critical pressure.
1. The critical temperature is defined as the temperature above which a substance cannot exist as a liquid.
2. The critical pressure is defined as the pressure above which a substance cannot exist in liquid state when it is at critical temperature.
17. Write the critical conditions of water.
1. Freezing temperature of water at atmospheric pressure = 0oC = 273.15 K
2. Boiling temperature of water at atmospheric pressure = 100oC = 373.15 K
3. Critical temperature of water = 373.946 oC = 647.1096 K
4. Critical pressure of water = 220.64 bar
18. State the changes in volume and temperature of water during steam formation.
1. During melting stage and vapourising stage, the temperature remains constant. The temperature increases during solid stage and superheating stage.
2. The volume increases during solid stage, liquid stage, vapourising stage and superheating stage. The volume decreases during melting stage.
19. Draw the phase diagram for water.
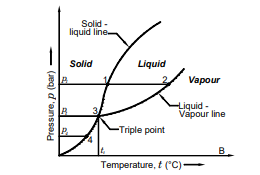
20. What it triple point? State its condition for water.
Triple point is a point at which a substance exists in three forms such as solid, liquid and vapour.
For water :Triple point pressure, pt = 4.58 mm of Hg (611.2 Pa)
Triple point temperature , tt = 0.1oC (273.16 K)
21. Define specific volume of water.
Specific volume of water is defined as the volume of unit mass of water at the given pressure and temperature. It is denoted by the symbol ‘ f v ’ and is expressed in m3/kg.
22. Define specific volume of steam.
Specific volume of steam is defined as the volume occupied by unit mass of steam at the given pressure and temperature. It is expressed in m3/kg.
